20 Tips for Soldering Inductor Components
![]() 2024.3.6
2024.3.6
 Articles
Articles
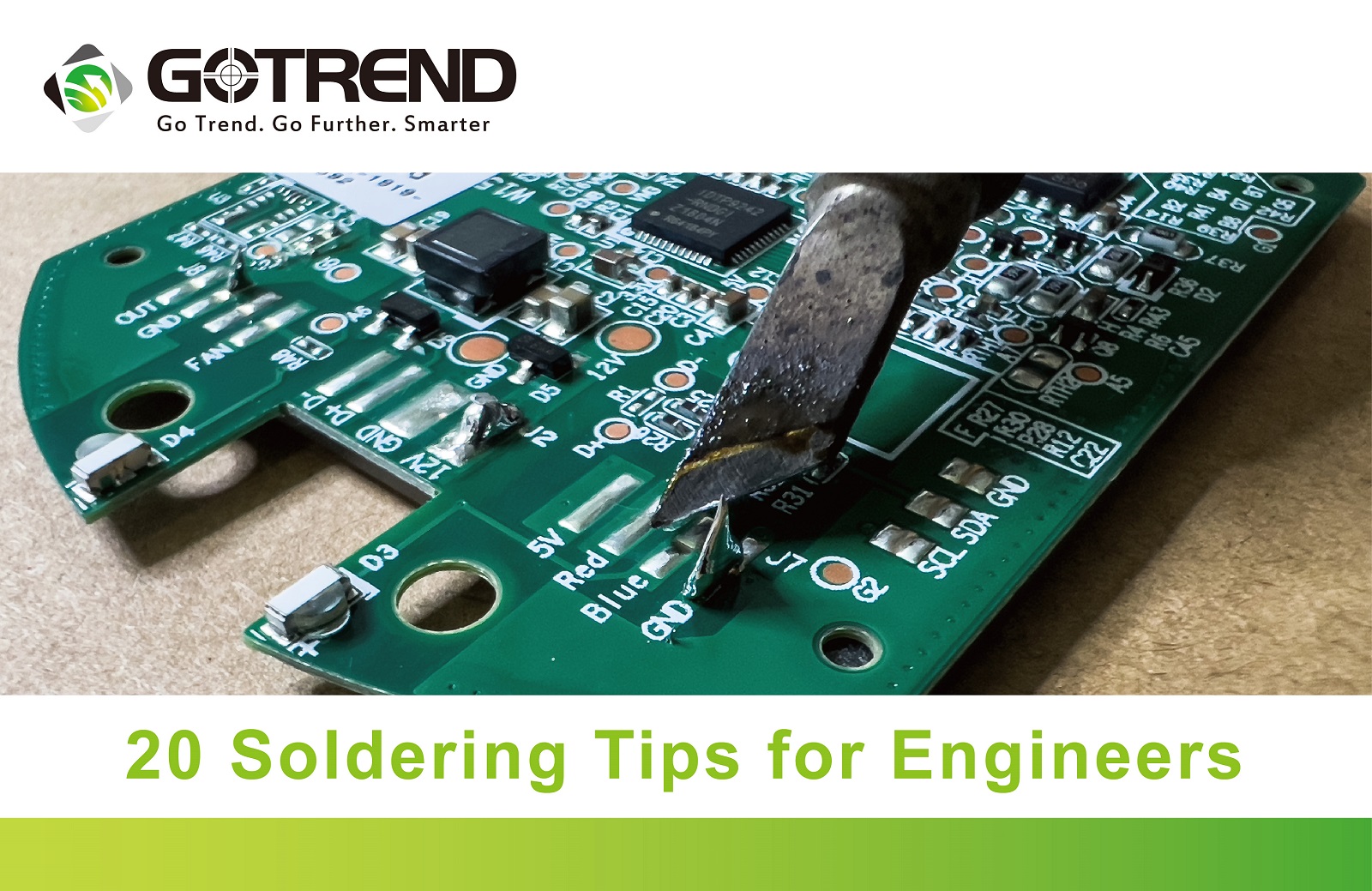
Inductive components are the main product of GOTREND , and soldering is a crucial process in the production of inductive components. It is also one of the fundamental skills in working with electronic circuits.
Soldering is an essential skill, and although beginners can successfully solder circuit boards and other basic components, mastering the art of soldering opens up new possibilities for engineers. Therefore, if you are unsure about soldering or even apprehensive about handling a soldering iron, here are some soldering tips and guidelines to help you get started.
Solder, What Is It, and How Is It Done?
Soldering is the process of joining two pieces of metal by heating them to an appropriate temperature and connecting them. This is achieved by using a filler material, which, upon cooling, fuses the originally separate structures into a single entity.
20 tips for Soldering
1. Before soldering, it is essential to understand the properties of your solder, the items you need to solder, and the tools and soldering materials involved. Given the various tools and soldering materials available, choosing the right tools and materials is crucial to efficiently complete the soldering task.
2. Before commencing the soldering process, it's advisable to conduct a first article trial on some old or defective products.
This ensures that materials, tools, and methods are correct before proceeding with soldering. This way, you can avoid any losses and mitigate risks associated with the product.
3. Soldering operators should have access to training materials on soldering tools and methods to enhance their soldering skills. Practice your soldering techniques by working with various types of materials, starting with simple materials, to gain hands-on soldering experience.
4. When soldering inductors on a PCB or near IC chips, caution is required, as excessive heat can potentially damage sensitive components or leave traces of circuit board burn marks. Unlike direct soldering of components, a socket needs to be soldered onto the circuit board first, and then the component is inserted into the socket.
Lead-based solder wire has a melting point between 183-245°C, while lead-free solder wire has a melting point of 217-227°C.
5. Safety precautions for the operator are essential during the soldering process. Prior to soldering, wearing safety goggles is crucial to prevent hot solder from splashing into your eyes, potentially causing severe injuries.
6. Soldering also requires a specific environment. It is necessary to work in a well-ventilated area because the fumes produced during soldering can be harmful to your health, particularly when using lead-based solder. Work either outdoors or employ an exhaust fan during soldering to expel fumes.
7. Inductive components also require soldering with a soldering iron. It goes without saying that soldering irons get very hot, so avoid placing them on your desk or in unsafe locations. They remain hot, so exercise caution. Lay non-flammable material in your work area to prevent hot solder from dripping, as it may pose a fire hazard.
8. Soldering materials come in two types: lead-based solder and lead-free solder.
While you are free to choose either type based on your preference, it's important to note that, although lead-free solder is safer due to its non-toxic nature, many believe that lead-based solder provides relatively better performance.
All electronic components by GOTREND are manufactured using lead-free solder.
9. The nature of soldering materials, whether lead-free or leaded, can also be identified through a specific method. To determine if solder contains lead, you can heat it. After cooling, lead-based solder will have a shiny appearance, while lead-free solder will exhibit a noticeable contrast.
• Characteristics of lead-based solder wire: Bright solder joints, good wetting properties, easy tinning ; no-spatter when using flux, uniform flux distribution.
• Characteristics of lead-free solder wire: Solder joints appear concave, solder points are full, smooth, and free from pinholes or rosin residues.
10. When soldering with a soldering iron or soldering wire, it is advisable to use rosin flux to prevent oxidation of the solder. Rosin flux is a non-acidic, resinous substance extracted from tree sap. Applying this flux to the workpiece before soldering helps prevent oxidation.
11. How do we choose between a soldering iron and a soldering gun for our work?
Soldering irons are highly convenient, especially when working with fine wires and small components, particularly in circuit boards and tight spaces. However, soldering guns are better suited for both fine and heavy-duty wires due to their greater power.
12. Soldering guns and soldering irons are not the same; soldering guns have specialized tips and tend to be more expensive. So, if you want to use a soldering gun but find the price too high, you can take a 7-strand uninsulated wire and cut a 5-6 inch section of it. Bending these wires into the exact same shape as an alternative to a soldering gun is a very cost-effective technique.
13. If you find yourself in a situation where you need to solder without access to any power or tools, it's still possible. You can use a Portable butane torch with a suitable adapter on top. This device can easily melt solder.
14. When working with soldering applications that require the use of cables or wire sleeves, the ends of the soldering wire should have the shrink tubing removed. The area on the object to be soldered needs to be stripped of its insulation, exposing the metal surface.
15. Welding torches have a life, and to extend the life of the soldering tip, it's important to keep it clean and tinned. Heat the tip and apply a small amount of solder to cover it. Then, wipe it with a damp sponge, removing everything except for a thin layer of solder. This helps the tip last longer and improves heat transfer.
16. If you wish to prolong the durability of soldered joints, especially for wire connections, you can apply a suitable amount of silicone paste to the joint and heat shrink tubing. Then, use a heating tool, starting from the center and gradually moving outward, to ensure thorough removal of excess silicone resin inside the tubing. This enhances the stability and waterproofing of the joint.
17. Avoid touching the soldered joint until it has cooled completely. Disturbing the joint while the solder is still in a liquid state may lead to cracks forming in the solder or air gaps. Therefore, waiting for the joint to cool completely is an important safety step.
18. During the soldering process, it's advisable to position the wire beneath the solder and add an appropriate amount of solder between them rather than directly dropping solder onto the wire. Otherwise, the solder may not penetrate the interior of the wire, resulting in a poor electrical connection. By following the correct operating procedure, you can ensure that the solder fully penetrates the wire's interior, forming a reliable electrical connection.
19. After completing the soldering, it's important to trim the leads on top of the solder joints to prevent them from coming into contact with nearby leads, which could potentially cause a short circuit. Therefore, lead trimming is a crucial step to ensure the proper operation and safety of the circuit.
20. During the soldering process, it's essential to ensure that the melted solder doesn't form spots that lead to the cooling of the solder joint. Additionally, the smoother the adhesion on the surfaces of the PCB and components, the better the connection. Therefore, for achieving a good quality connection, precise operation during the soldering process and attention to the formation of solder joints are necessary.
Quality Assessment After Soldering
Solder points are considered unqualified when they :
1. Insufficient or excessive amount of solder.
When the amount of solder is not enough to wet the surface of the wire or component, or too much solder causes uneven or pointed solder joints, these conditions will affect the quality and electrical performance of the solder joints.
2. Uneven solder joint surface or the presence of bubbles.
If the solder joint surface is uneven or contains bubbles, it indicates that the solder did not adequately wet the wire or component surfaces, or that air was not completely eliminated during the soldering process. This condition can potentially lead to poor electrical connections or a reduction in the durability of the solder joint.
3. Inadequate securing of wires or components.
If wires or components are not securely fastened, it may impact the quality and stability of the solder joint. In such cases, the solder joint may become loose or detached during subsequent use.
4. Wires cut too short or too long.
Cutting wires too short or excessively long can result in poor electrical connections or affect the appearance. The correct wire length should allow for sufficient wetting of the wire ends and component surfaces with solder while maintaining an appropriate spacing for future maintenance and component replacement.
High temperature risk warning and feedback requirements for inductive device
In electronic devices, inductive components are crucial elements involved in the storage and release of energy.
However, improper temperature and time control can have adverse effects on the inductive sensor itself, even leading to damage. To ensure the normal operation of inductive components and maintain the overall performance of the equipment, please take note of the following tips regarding temperature, time, and issue feedback.
1. Temperature and time anomalies :
Inductors are highly sensitive to temperature changes. Elevated temperatures may alter their internal physical properties, such as aging, expansion, or burning of coil insulation, resulting in decreased insulation performance and ultimately leading to abnormal readings or short circuits.
2. Physical Impact :
During the soldering or rework process, repeated soldering can subject the components to physical impact. Pressures, falls, and external forces during the soldering process may lead to coil deformation, resulting in abnormalities such as short circuits or open circuits.
3. When encountering product quality doubts, in order to ensure the correct analysis of the real cause, it is recommended that the user keep the original PCBA in its original state, and contact the professional engineering and quality team of GOTRNED for precise measurement and disassembly, and our professional team will conduct an in-depth analysis according to the actual situation to accurately find out the root cause of the problem.
Related articles :
• What is a pulse transformer?
• Ring Core Common Mode Filter【GTCM Series】 Stabilize signals, efficiently filter out noise interference.
• What is the difference between lead-free solder and leaded solder ?
 GOTREND Technology Co., Ltd.
GOTREND Technology Co., Ltd.


