What is the safety distance for high-frequency transformers?
![]() 2024.7.10
2024.7.10
 Articles
Articles
1、What is the safety distance for high-frequency transformers?
The safe distance for high-frequency transformers refers to the design distance between internal and external structures. It includes electrical clearances, creepage distances, and insulation penetration distances to ensure proper insulation and isolation, thereby avoiding safety risks such as electric shock, discharge, or breakdown.
Common IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) standards establish safety distance requirements between primary circuits to secondary circuits, primary circuits to the core, and secondary circuits to the core in high-frequency transformers. When designing and manufacturing high-frequency transformers, it's necessary to refer to applicable safety standards and specifications to determine appropriate safety distance requirements. These requirements may involve electrical clearances, creepage distances, and the selection of insulation materials.
• Electrical Clearance :
Electrical clearance refers to the shortest distance between two conductors. It directly measures the physical distance between two conductors and is typically used to ensure that no discharge or breakdown occurs between the conductors under a given voltage. Electrical clearance is usually achieved through air or other insulation mediums.
• Creepage Distance :
Creepage distance refers to the shortest distance measured along the surface of insulation between two adjacent conductors. It represents the actual distance along a curved, curved, or straight path on the insulation surface.
Due to polarization of the insulation material surrounding the conductors, it prevents electrical arcing, breakdown, and other electrical faults. It is designed to prevent current from creeping on the insulation surface. The size of creepage distance depends on the characteristics of the insulation material and the requirements of safety standards and specifications.
• Insulation Penetration Distance :
The insulation penetration distance refers to the distance at which insulation material extends between two conductor components. It provides additional insulation protection to prevent electrical faults and discharges. For working voltages not exceeding 50V, the requirements for insulation penetration distance depend on the type of insulation.
There are no specific thickness requirements for primary insulation.
For additional insulation, as well as reinforced insulation that needs to withstand mechanical stress, the minimum thickness should be more than 0.4 mm.
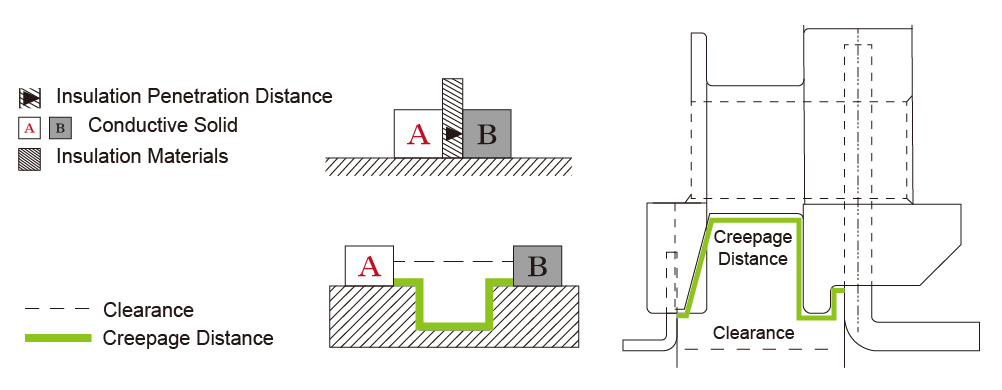
Transformer Safety Clearance Diagram
2、In high-frequency transformers, what are some common materials used for insulation and safety distances?
A. Insulation Tape :
Insulation tape is a material used to wrap wires, insulate conductors, and other electrical components. Its purpose is to provide additional insulation protection, preventing electrical short circuits or discharges between wires or between wires and other conductor components.
B. Bobbin :
A bobbin is a component used in high-frequency transformers to support and secure coils. Typically made of insulation material, it helps in arranging coil layouts, providing proper safety distances, and securing coils to the core.
C. Margin Tape :
Margin tape is an insulation tape used to provide insulation isolation between the edges of coils or windings in the bobbin. Its purpose is to prevent electrical short circuits or discharges between coils or between coils and other conductor components. Therefore, the width of the margin tape can increase the electrical isolation distance inside the transformer.
D. Wire :
Wire constitutes the conductive part of high-frequency transformers. Different types of wire, such as enamel-coated wire, triple-insulated wire, and motor wire, have varying insulation specifications. Additionally, sleeving or tape can be used to enhance insulation specifications and distances.
E. Varnish :
Varnish is an insulating coating used to encapsulate windings or coils, providing additional insulation and fixation. It enhances the insulation performance of coils, preventing arcing and electrical faults.
F. Nomex :
Nomex is a high-temperature insulation material commonly used in high-frequency transformers, known for its excellent heat resistance and insulation properties. It is utilized to insulate coil windings, preventing insulation breakdown and penetration during temperature spikes.
G. Tube :
A tube is a tubular insulating material used to encase wires, windings, or other electrical components, providing additional insulation and mechanical protection. It helps prevent wires from damage due to external environments and electrical shorts.
In summary, these structural component materials play various roles in high-frequency transformers, including providing insulation protection, securing and supporting coils, guiding magnetic fields, and preventing electrical shorts and discharges. They work together to ensure the normal operation and safety performance of high-frequency transformers.
3、 Certification Marks and IEC Standards
Safety distance standards for high-frequency transformers are clearly stated and guided in different regulations to avoid poor design or improper use.
Most countries have their own safety regulations. Due to differences in geographical environments and voltages between countries, safety standards are not entirely the same. Certification marks and International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) standards are different concepts and play different roles in product certification and standardization.
• Safety Certification Marks :
Certification marks are granted by certification bodies in various countries or regions to demonstrate that products comply with the relevant safety regulations and standards. These certification marks are typically issued by third-party certification bodies, and products are tested and evaluated to confirm compliance with safety requirements.
Common certification marks include UL/CUL, GS, PSE/S, CCC, etc. These marks are often requirements for products to enter specific markets, proving that the products have passed relevant safety tests and certifications.
• I E C (International Electrotechnical Commission) Standards :
IEC standards are international standards developed by the International Electrotechnical Commission, covering a wide range of electrical, electronic, and information technology fields.
These standards aim to regulate the design, performance, and testing requirements of products to ensure their safe, reliable, and effective use. IEC standards are not certification marks but a series of technical specifications and guidelines for manufacturers, designers, and engineers to reference and follow.
4、Differences in Safety Standards
Taking EN 60950-1 and IEC 60601-1 as examples, these two are safety standards for different types of equipment. EN 60950-1 is primarily for Information Technology Equipment (I.T.E), covering devices like computers, printers, and network equipment.
On the other hand, IEC 60601-1 focuses on medical equipment, such as medical instruments and devices. It emphasizes the safety and electrical performance of medical equipment in patient contact areas.
As shown in Table 1 , voltage testing is based on an AC voltage input of 250 VAC for power supplies. The power supply insulation level under IEC60601-1 is stricter compared to EN60950-1.
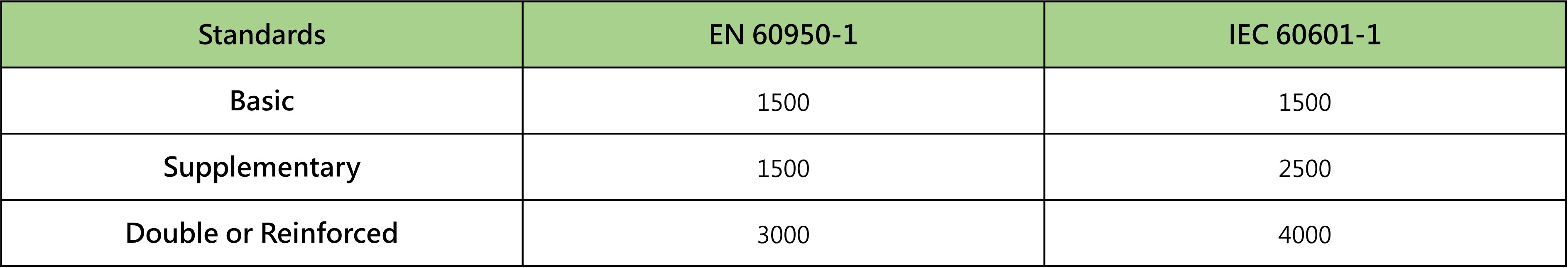
( Table 1 )
From Table 2, it's evident that medical equipment requires larger insulation distances and creepage distances, with voltage tests being more stringent to provide higher safety levels.
Insulation distance refers to the shortest distance between two conductors, while creepage distance is the shortest distance measured along the insulation surface between two conductors.
These requirements aim to ensure that through these tests during normal operation, the safety performance of the equipment under both normal and abnormal conditions can be determined, thereby reducing potential risks to patients and operators.
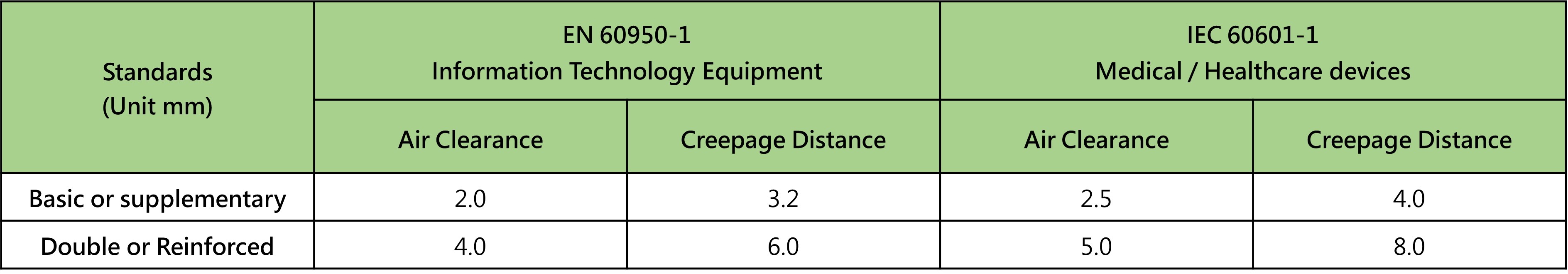
( Table 2 )
Related articles :
• What is Transformer Bobbin? What is transformer bobbin used for?
• GOTREND Wire-Wound Inductors【GNLT Series】Ideal for Communications, Radar, and Wireless Applications
• GOTREND BMS Magnetic Component Solutions
 GOTREND Technology Co., Ltd.
GOTREND Technology Co., Ltd.


