What is Transformer Bobbin? What is transformer bobbin used for?
![]() 2024.6.25
2024.6.25
 Articles
Articles
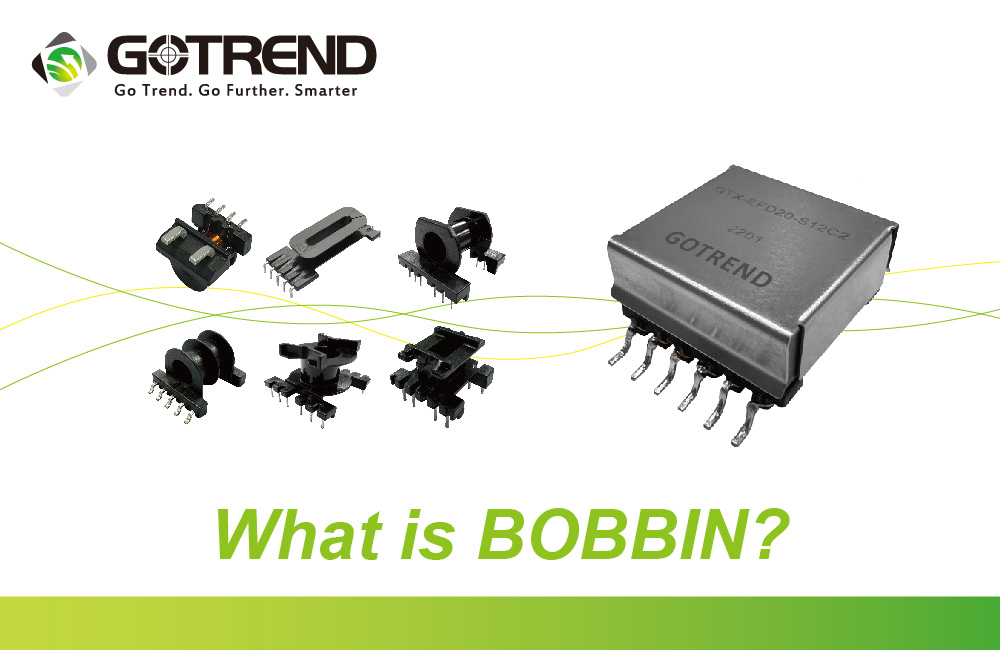
1、Definition of a Bobbin:
A bobbin, also known as a transformer frame or core frame, is a component of transformer structures. It is paired with different shapes of magnetic materials to support the winding coils and provide insulation protection. Standardization and safety of bobbins play a crucial role in transformer manufacturing.
The bobbin plays a critical role in transformers. It is a supporting structure used to secure and protect the winding coils. The shape and material selection of the bobbin depend on the design and application requirements of the transformer. It can be made of plastic or metallic materials to ensure insulation and durability.
2、The main functions of the bobbin are as follows:
The bobbin plays multiple crucial roles within the transformer.
A、Provision of winding space :
The winding slots in the bobbin provide space for the winding of coils and ensure proper routing of the wires.
B、Matching Different Shapes of Iron Cores :
The bobbin is designed with different corresponding shapes based on the appearance and central column shape of the iron core. This ensures proper alignment and fit between the bobbin and the iron core, optimizing transformer performance.
C、Supporting Copper Wire Winding :
In addition to using plastic molds, the bobbin can also utilize metal molds to provide support for copper wire winding in DIP or SMD configurations. This ensures solder connections between copper wires and circuit boards.
D、Marking PIN Foot Positions :
Bobbins may feature protrusions, indentations, chamfers, or colored dots to mark the starting position of PIN feet, ensuring correct orientation during assembly.
E、Featuring Raised Barriers :
Bobbins typically have raised barriers at the bottom to secure and maintain evenness and distance during assembly onto the board. Proper spacing helps prevent damage to wire insulation during soldering.
F、Ensuring Insulation and Electrical Safety :
Bobbins play a crucial role in ensuring insulation and electrical safety within transformers. By providing insulation layers and safe distances, they prevent short circuits or electrical hazards between different windings and components.
These functions highlight the importance of bobbins in transformer manufacturing. They contribute to proper winding, alignment, insulation, and assembly processes, thereby enhancing the efficiency and safety of transformers. Careful consideration of factors such as core shape, wire routing, PIN foot positions, and insulation requirements is essential when designing and applying these features.
3、Types of Plastic for Bobbins :
Bobbins primarily use plastic as the raw material, molded through compression or injection methods.
Plastics can generally be classified into two types :
Thermoplastics and thermosets. Common plastic materials include phenolic molding compound (PM), nylon (PA), polyethylene terephthalate (PET), polyoxymethylene (POM), and other engineering plastics. Different materials possess varying characteristics such as hardness, temperature resistance, and flexibility, which directly impact the performance of the bobbin.
Common materials for bobbins include :

A、Phenolic Molding Compound (PM), commonly known as Bakelite :
PM is a common material in transformers and falls under the category of thermosetting plastics. It boasts high stability and hardness, resisting deformation while exhibiting excellent temperature resistance. It typically withstands temperatures up to 150 degrees Celsius, and some formulations can even endure temperatures exceeding 300 degrees Celsius.
It has a smooth surface appearance but is prone to fracturing and cannot be recycled. PM is often used in traditional transformer applications requiring high temperature resistance.
B、Nylon, also known as PA(Polyamide):
Nylon is a thermoplastic material. While it has lower stability and is prone to deformation and water absorption, it possesses good flexibility and high impact strength, making it less susceptible to breakage. Nylon can typically withstand temperatures up to approximately 90 degrees Celsius. It has a smooth, semi-transparent appearance and is commonly used in applications that demand high oil resistance.
C、Plastic, also known as Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) :
PET is a thermoplastic polymer known for its high stability and good hardness. It resists deformation, has some degree of flexibility, and is less prone to fracturing. It typically withstands temperatures of about 150°C and maintains good performance over a wide temperature range. Plastic exhibits excellent insulation properties and can resist corrosion from weak acids. Its surface appearance is not smooth and is widely used in electronic insulation and aesthetics, commonly found in traditional transformers.
D、Plastic, also known as Polyoxymethylene (POM) :
POM is a thermoplastic polymer. While it has lower heat stability, it offers excellent overall performance, boasting high hardness, resistance to deformation, low water absorption, and good elasticity and fracture resistance. It typically withstands temperatures of about 100 degrees Celsius and decomposes beyond 200 degrees Celsius, requiring attention to its corrosion resistance in design. Due to its superior overall performance, it finds broad applications, commonly used in high-frequency transformers.
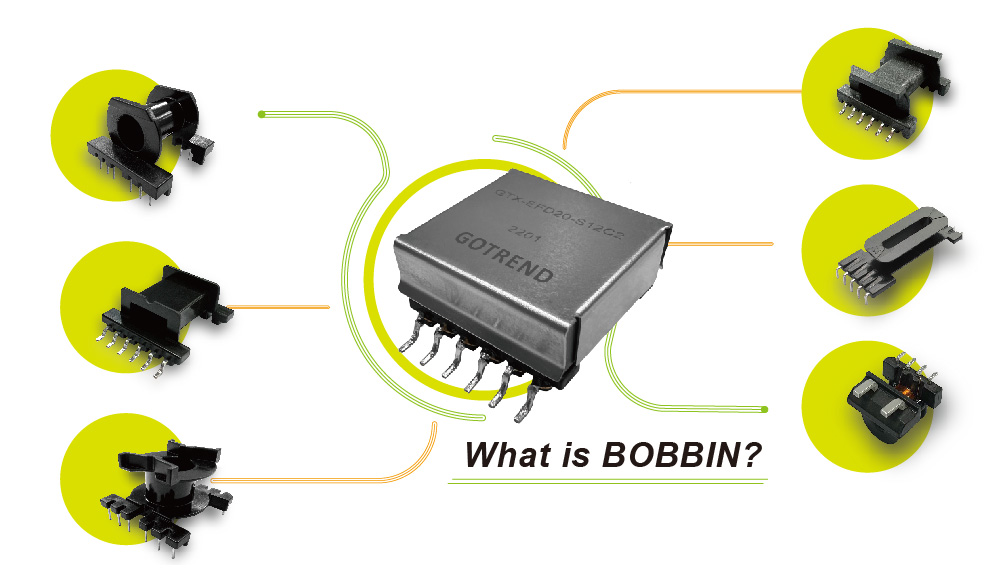
4、Types of Bobbin Appearances :

Bobbins come in various appearances, assembly methods, and special types, providing a wide range of options to meet the requirements of various electronic products. Designers need to carefully consider the product design requirements, manufacturing processes, and functional demands to choose the most suitable bobbin type and assembly method, thus achieving optimized design and performance.
Common types include :
A、Types of Core Appearances :
The appearance of cores used in bobbins can be categorized into various types, such as EI, EE, EF, ER, RM, PQ, UU, etc. These types are named based on the shape and structure of the core laminations. Each type comes with different heights and sizes to meet various assembly requirements.
For instance, the EI type core features "E" and "I" shaped laminations with a central gap, while the EE type core has "E" shaped laminations without a central gap between the two laminations.
B、Vertical and Horizontal Classification :
Bobbins can also be classified into vertical and horizontal types based on the assembly direction. The choice between vertical and horizontal bobbins depends on specific installation requirements, space limitations, and application needs.
• Vertical bobbins have their core assembly direction perpendicular to the base, meaning the core is placed upright. This structure is typically used for applications requiring upright installation, such as vertical transformers or vertical inductors.
• Horizontal bobbins have their core assembly direction parallel to the base, meaning the core is laid flat. This structure is typically used for applications requiring flat installation, such as horizontal transformers or horizontal inductors.
C、SMD, DIP, and No-PIN Foot Assembly Methods :
Bobbins can be assembled using methods such as SMD (Surface Mount Technology), DIP (Dual In-line Package), and No-PIN Foot.
SMD is an advanced assembly technique where components are directly mounted onto the surface of a printed circuit board (PCB). SMD components are known for their compact size, high density, and reliability.
DIP is a traditional assembly method where component pins are arranged in two rows and inserted into corresponding holes on the PCB.
No-PIN Foot packaging refers to components where pins are not directly visible during packaging or where flying wires are used to connect the pins without going through the circuit board.
The choice of assembly method depends on product design requirements, manufacturing processes, and functional needs of the components.
D、Multi-Slot Bobbins :
Bobbins can also be classified based on the number of slots, including single-slot, double-slot, and multi-format, among others. These multi-slot bobbins are used for insulation and isolation to meet different electrical requirements. Multi-slot bobbins offer greater flexibility and choices to meet the component assembly requirements of complex electronic products.
E、Special Types of Bobbins :
Advanced designs also include special types of bobbins, such as recessed bobbins with PCB cutouts or bobbins embedded with copper wires. These special bobbin types are typically designed for specific requirements to meet more complex assembly and circuit layout needs.
Additionally, there are special types of bobbins like the two-piece stock and bobbin set, which extend based on different demands, providing more design options.
Related articles :
• How to Calculate Inductor Ripple Current ΔIL?
• What requirements should the solder joints of lead-free solder meet?
• GOTREND【GSFH Series】high-current molded inductors-Excellent performance, high stability, versatile applications.
 GOTREND Technology Co., Ltd.
GOTREND Technology Co., Ltd.


