What is the Dot Convention?
![]() 2025.1.17
2025.1.17
 Articles
Articles

1、Definition of the Dot Convention
The dot convention is a standard method used in circuit analysis and coil design for inductors, transformers, coupled inductors, and common mode chokes. It identifies the start and end points of a coil winding, ensuring consistent representation of coil polarity.
2、Basic Principles of the Dot Convention
(1) Marking the Dot Location :
A dot is typically placed on the product or circuit to indicate terminal 1 of a winding. On circuit diagrams, each coil's starting terminal is marked with a dot.
GSTC201608P-S-SERIES
.jpg)
GTX-EP13P-S10M
.jpg)
(2) Relative Position of Dots :
The relative position of the dots determines whether the coupling between coils is forward or reverse. Alignment of dots indicates forward coupling, while misalignment signifies reverse coupling.
(3) Direction Identification :
The alignment of dots correlates with mutual inductance. When dots are aligned, the direction of mutual inductance is positive. Misalignment implies opposite directions.
3、Differences Between Forward Coupling, Reverse Coupling, and No Coupling
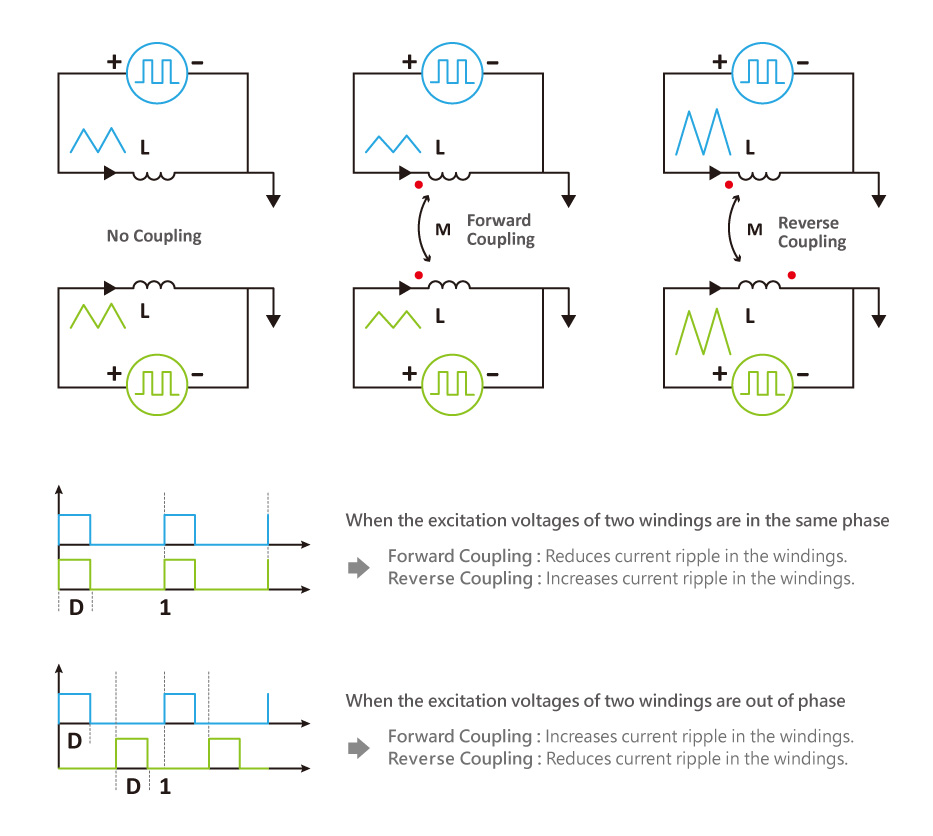
In manufacturing and design, the dot convention plays a critical role in standardizing processes, ensuring consistent production, and providing designers with a clear understanding of coil polarity to meet various application needs.
4、Why Do Some Inductors Follow the Dot Convention While Most Do Not?
In high-frequency applications, the dot convention becomes essential because the coil's geometry significantly impacts high-frequency performance and radiated EMI. Factors like symmetry and dot placement can notably affect component performance in high-frequency environments.
Conversely, in low-frequency applications, these differences have minimal impact on performance. As a result, the dot convention is often overlooked or deemed unnecessary, explaining why most inductors lack this designation in low-frequency scenarios.
GSTC201608P-S-SERIES
.jpg)
The dot convention provides a standardized, unified approach to eliminate confusion and ambiguity in describing coil mutual inductance. This practice is particularly valuable in the design and analysis of high-frequency coupled coils, transformers, and mutual inductors. In such applications, the dot convention ensures design accuracy and supports achieving desired performance targets.
Related articles :
• Design and Application of Common Mode Chokes
• What is a Flyback Transformer?
• Ferrite Wire-Wound Inductors【GNLD Series】Enhance Power Conversion Efficiency
 GOTREND Technology Co., Ltd.
GOTREND Technology Co., Ltd.


