Inductor thermal resistance ΘTH calculation,what is thermal resistance?
![]() 2022.11.24
2022.11.24
 Articles
Articles
Thermal resistance is a numerical value that indicates how easy it is to transfer heat. is the temperature difference between any two points divided by the amount of heat flowing between the two points. (Heat flowing per unit time)
A high thermal resistance means that heat is difficult to transfer, while a low thermal resistance means that heat is easy to transfer.
Thermal resistance ΘTH calculation
The IDC value is the DC bias when the inductor temperature rises to Tr°C. The datasheet also indicates its DC resistance value RDC at 20°C.
The temperature coefficient of the copper wire is about 3,930 ppm, and the resistance value is RDC_Tr = RDC (1+0.00393Tr) at the temperature rise of Tr.
Its power consumption is PCU = I2DCxRDC.
This copper loss dissipates the power dissipation on the surface of the inductor, and the thermal resistance of the inductor ΘTH can be calculated :
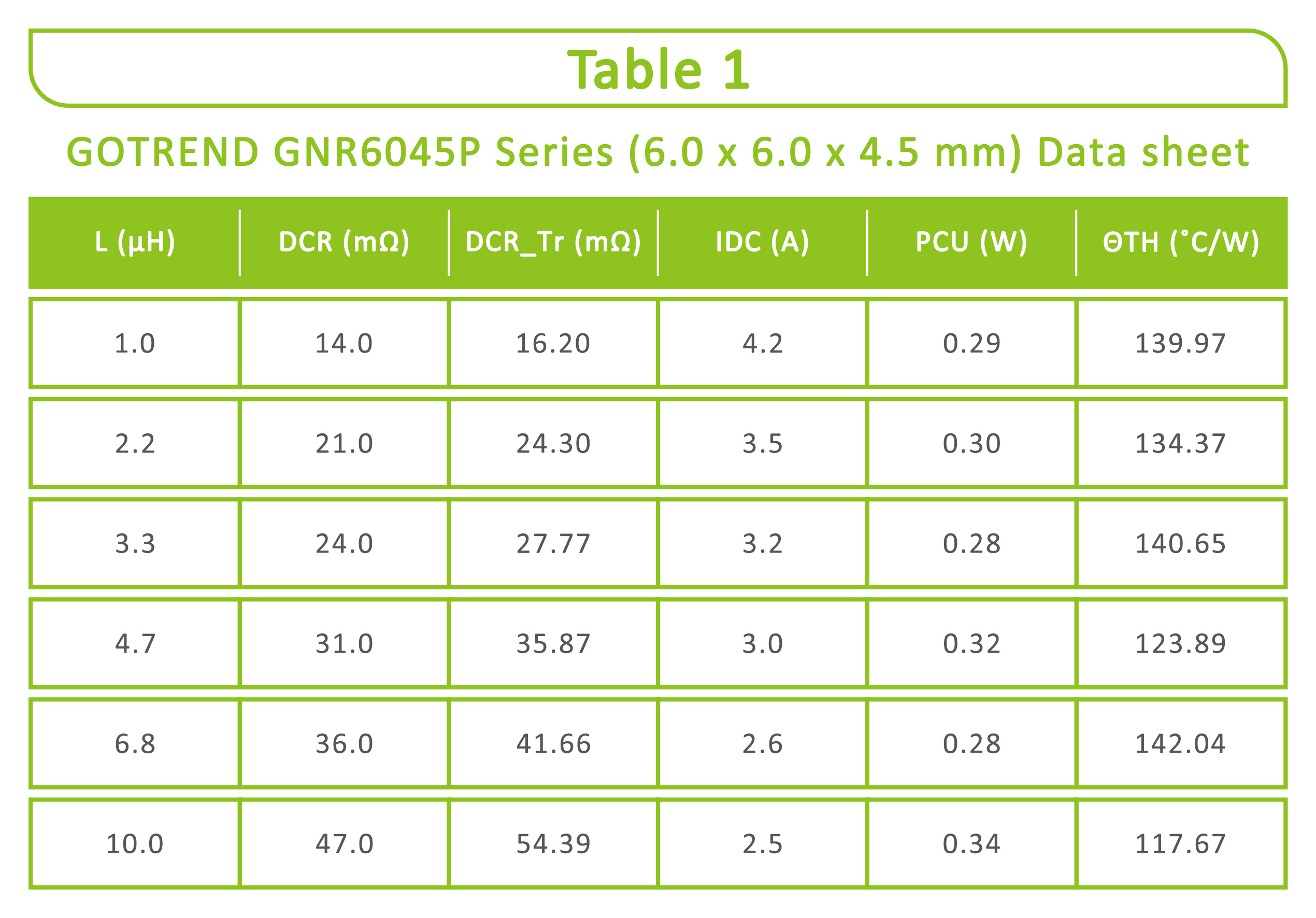
【Table 1】 - Refers to the data sheet of the GOTRND GNR6045P series (6.0x6.0x4.5mm) and calculates the thermal resistance at a temperature rise of 40°C.
Obviously, the inductors of the same series and size have the same thermal resistance calculated because the surface heat dissipation area is the same; In other words, the rated current IDC for different inductors can be estimated. Different series (packaged) inductors have different thermal resistances.
The following chart shows the GNR6045P series, the thermal resistance of the inductor at 40°C temperature rise.
Obviously, the inductors of the same series and size have the same thermal resistance calculated because the surface heat dissipation area is the same; In other words, the rated current IDC for different inductors can be estimated. Different series (packaged) inductors have different thermal resistances.
The following chart shows the GNR6045P series, the thermal resistance of the inductor at 40°C temperature rise.
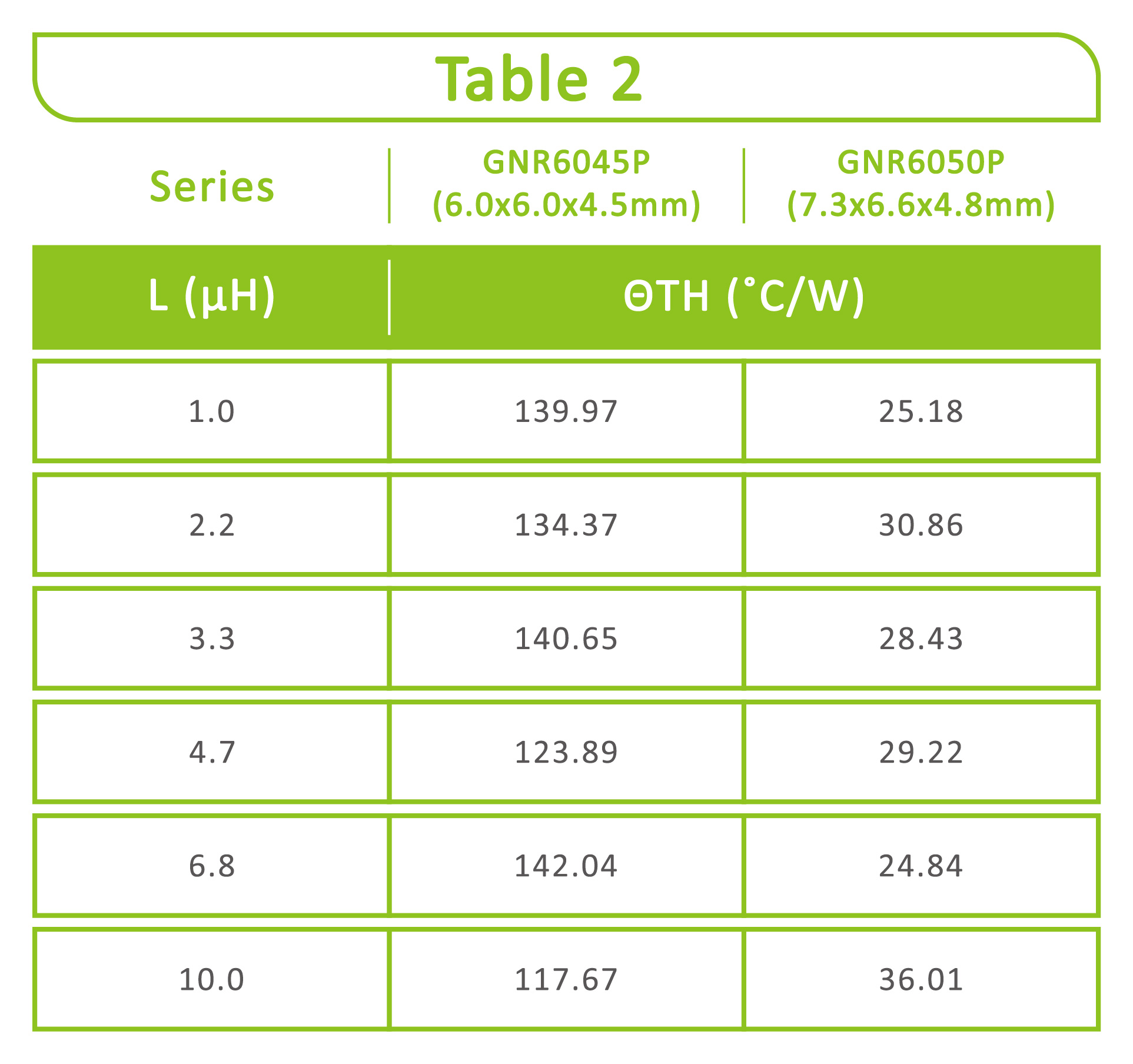
Thermal resistance comparison of inductors from the GOTREND GNR6045P series (semi-shielded) and GSTM6050P series (molded). The larger the thermal resistance, the higher the temperature rise generated when this inductor flows through the load current; The converse is lower.
From this table, it can be seen that even if the size of the inductors is similar, the heat dissipation is better due to the low thermal resistance of the molding inductors.
This application file describes the basic formula for determining the thermal resistance of an inductor. At the same time, different packaging products will have different thermal resistance effects, and Molding packaging products will have good heat dissipation in comparison.
Related articles :
• APPLE MagSafe tangle dancing with Qi2 MPP
• What is copper loss? What is the skin effect ? The difference between Isat and Irms
• What is an inductor?
 GOTREND Technology Co.,Ltd
GOTREND Technology Co.,Ltd


