WPC Qi Wireless Charging Standard and Testing Certification
![]() 2024.9.10
2024.9.10
 Articles
Articles

1、What is the WPC Consortium ?
The Wireless Power Consortium (WPC) is a global collaborative organization composed of various independent companies. WPC established the Qi standard, an international benchmark for wireless charging pad and device compatibility. Any smartphone, camera, remote control, or other electronic product featuring the Qi logo is compatible with charging pads that also carry the same logo.
The "Qi" logo is a proprietary trademark of the WPC. Any wireless charging product that wishes to use this logo must first obtain authorization from the WPC. Unauthorized use of the Qi logo is considered infringement and may lead to penalties from the WPC or the removal of the product from the market. Additionally, wireless charging products that pass Qi certification meet the performance criteria outlined by the Qi standard, signifying that the product has reached a high quality level. For consumers, using Qi-certified products is safer and more reliable than using non-certified alternatives.
2、 What is the Qi Protocol ?
The Qi protocol, established by the WPC (Wireless Power Consortium), is a standard for short-distance, low-power wireless inductive power transfer, primarily designed for smartphones and other portable devices, providing wireless charging capabilities of 5 to 15 watts. The Qi logo, pronounced "chee," is phonetically identical to the word for "energy" or "life force" in Asian philosophy. The Qi standard ensures interoperability and compatibility between power receivers and transmitters, meaning any device that supports the Qi standard can be used with any Qi transmitter.
Compared to the previous generation of the Qi standard, the Qi2 upgrade introduces a new Qi logo and incorporates the Magnetic Power Profile (MPP) protocol as a technical branch within the Qi2 standard. Additionally, all certified equipment specifications must undergo identity verification and authorization mechanisms.
For manufacturers, Qi2 removes the requirement to follow the "reference coil types" for transmitters. Previously, the WPC maintained a reference coil library from which manufacturers had to select the appropriate coil type. Now, manufacturers no longer need to report the reference type of PTx coils during the certification process, simplifying the certification procedure and significantly enhancing design flexibility and freedom.
3、 Qi-V.1.3 Authentication Mechanism
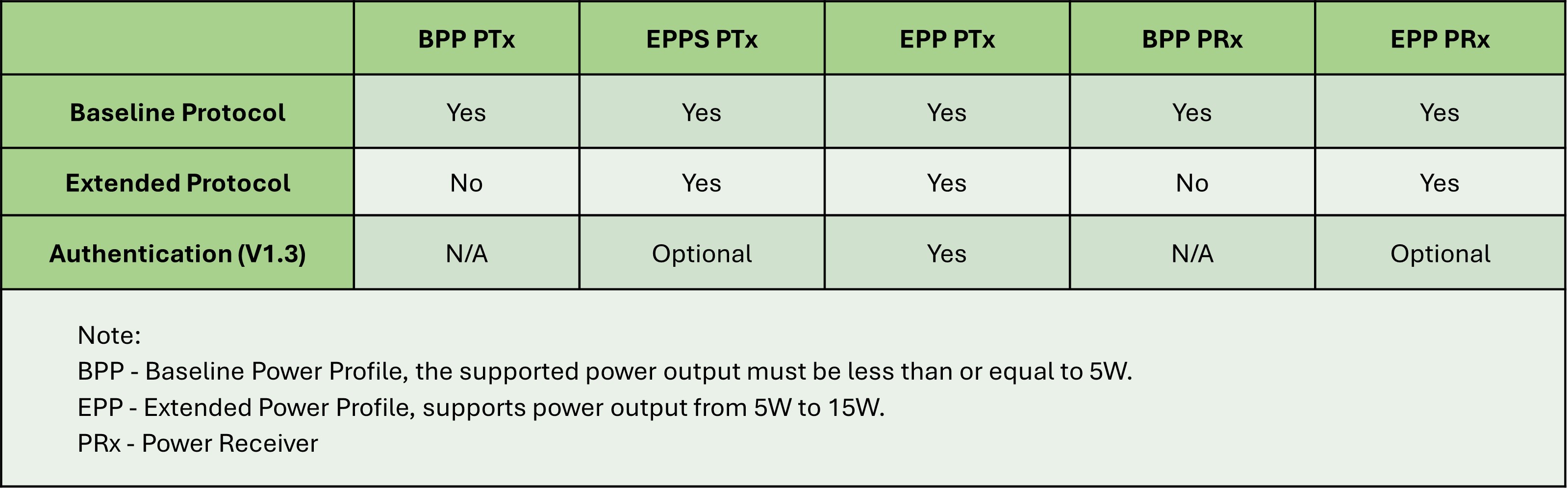
The WPC (Wireless Power Consortium) Qi-V.1.3 standard introduces product authentication as a new safety verification mechanism. This mechanism allows the receiving device to determine which charging protocol to use only after confirming that the transmitting device is a Qi-certified product. This means that if the authentication process between the receiving and transmitting devices fails, the receiving device can either refuse to communicate with the transmitting device or limit charging to the minimum power level (5W) to ensure safe usage across different wireless charging products.
Given that higher power transmission poses greater safety risks, the WPC has implemented different authentication requirements based on the output power of the products. For example, power transmitters that support medium power levels (EPP) must include the authentication mechanism under the Qi-V.1.3 certification, whereas transmitters or receivers that support lower power levels (BPP) do not require authentication. This approach ensures safer and more reliable interaction between devices, particularly in high-power transmission scenarios.
4、 Types of Qi Certification
Currently, the WPC continues to offer Qi certification for products across different versions, which can be categorized as follows:
• BPP ( Baseline Power Profile ) : Released before 2010, supporting power levels ≤ 5W, under the Qi 1.2 protocol.
• EPP ( Extended Power Profile) : Available from 2010 to 2021, supporting power levels of 5-15W, under the Qi 1.3 protocol.
• Samsung Proprietary Extension : 10W, under the Qi 1.3 protocol.
• MPP (Magnetic Power Profile) : Introduced in 2022, supporting power levels of 15-50W, under the Qi 2.0 protocol.
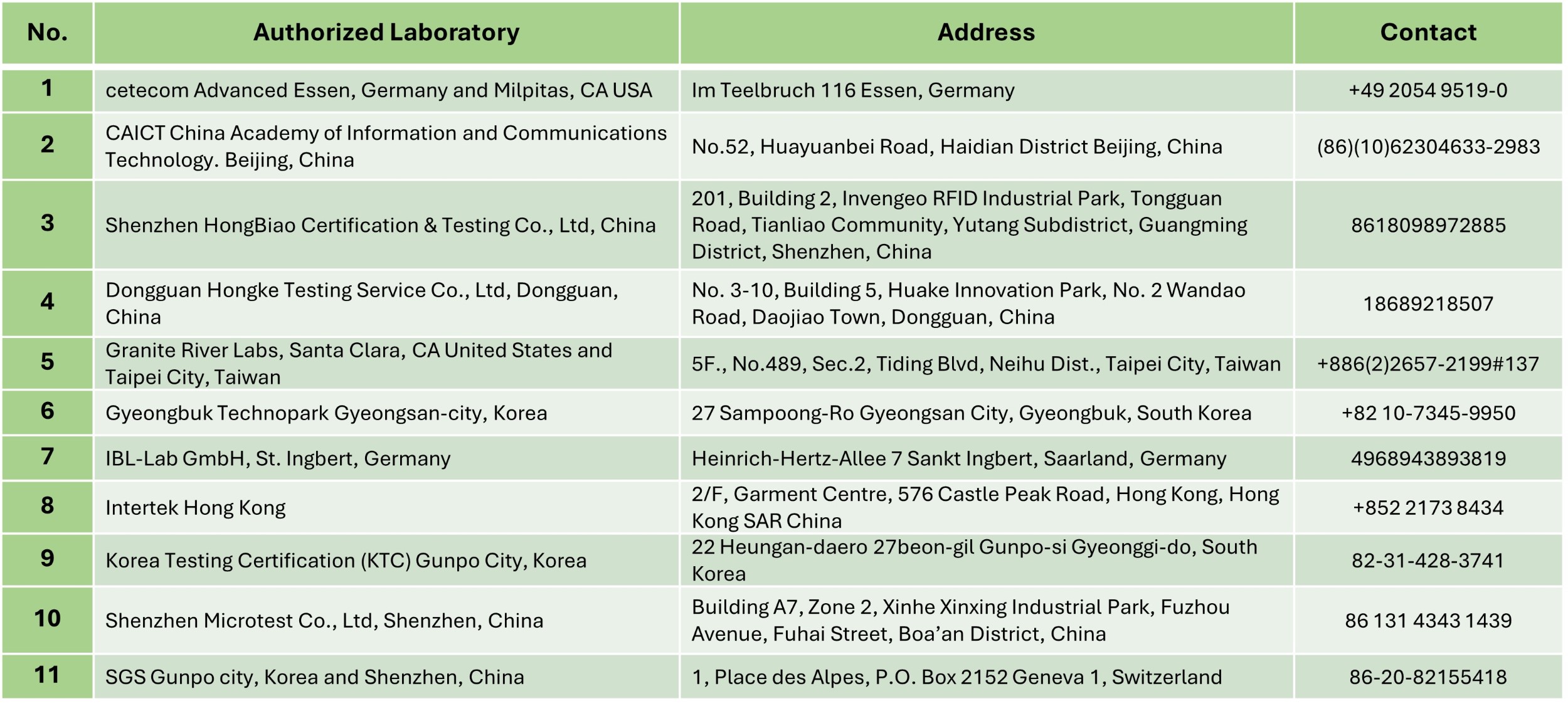
Qi Certification Laboratory Resources
The resources of ATL (Authorized Testing Laboratories) are as follows :
5、 Qi Certification Process and Testing Procedures
To apply for Qi certification for a product, the company must first become a member of the WPC (Wireless Power Consortium) and pay the corresponding membership fees. WPC offers different membership levels, including Small Business Member, Regular Member, Full Member, and Founding Member, each with varying fees and associated privileges.
Once the company becomes an authorized member, it needs to prepare five fully functional prototypes (using a Qi-certified wireless charging solution, such as those from NXP、旭鑫勝、凌陽、易充) and send them to a WPC-designated domestic certification laboratory, such as 安正、SGS、普瑞賽思. The solution provider and the client must then fill out the relevant product model, WPC member name, and certification type.
Depending on the output power, Qi-certified products are categorized into two types: BPP (Baseline Power Profile) and EPP (Extended Power Profile). BPP applies to products with an output power of 5W or less, while EPP is for products with an output power greater than 5W and up to 30W. After completing these steps, the testing fees must be paid.
Qi certification testing includes two main parts :
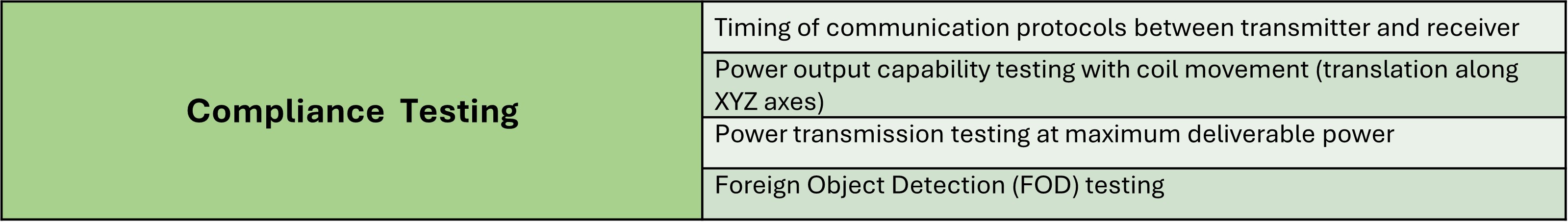
1.Compliance Testing
The Device Under Test (DUT) must be sent to an ATL (Authorized Testing Laboratory) for validation according to the Qi specifications set by WPC. This ensures that all Qi-certified products meet the latest established standards. The testing procedures are detailed in the table below.
2. Compatibility Testing (IOP)
After completing compliance testing, the Device Under Test must be sent to the Interoperability Test Center (IOC) for compatibility testing with hundreds of Qi-certified products. This ensures that all transmitters and receivers bearing the Qi logo on the market can establish wireless charging communication protocols. The testing details are as follows :
.jpg)
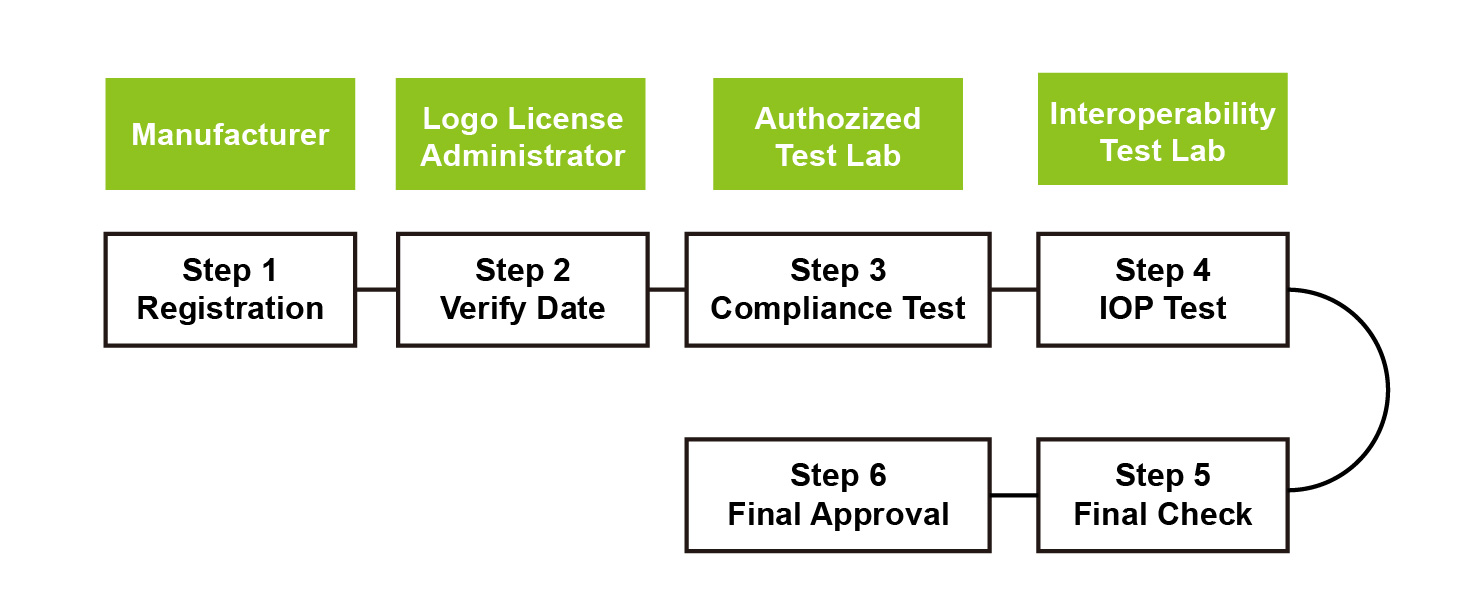
In addition to the aforementioned functional tests, the complete Qi certification process is as follows :
1. The manufacturer fills out product information and selects an Authorized Test Laboratory (ATL) and an Interoperability Test Center (IOC).
2. The Logo License Administrator (LLA) verifies that the information submitted in the first step is accurate.
3. The ATL conducts compliance testing and uploads the results.
4. The IOC conducts compatibility testing and uploads the results.
5. The manufacturer reconfirms the product information, model, and appearance.
6. After the LLA verifies that the test results and data are correct, the certified product will be listed on the certified products page.
6、 Qi Power Profiles– BPP & EPP
With the widespread adoption of wireless charging products, market demands for charging efficiency have significantly increased. To address this need, the Wireless Power Consortium (WPC) categorized products into Baseline Power Profile (BPP) for low power output and Extended Power Profile (EPP) for medium power output when establishing the Qi wireless charging standard. Due to the higher power output of EPP, there can be safety risks if used with products that do not comply with the Qi standard.
As a result, WPC released the Qi-V.1.3 standard in early 2021. Compared to the previous Qi-V.1.2.4 version, the Qi-V.1.3 standard mainly focuses on enhancing testing rigor and addressing safety issues through a verification mechanism. The following sections will outline the definitions of products with different power outputs and provide details on the verification process.
 GOTREND Technology Co., Ltd.
GOTREND Technology Co., Ltd.


