What is the principle of transformer and voltage conversion?
![]() 2022.6.16
2022.6.16
 Articles
Articles
What is a transformer? How is electricity converted ?
The structure and composition of the transformer :
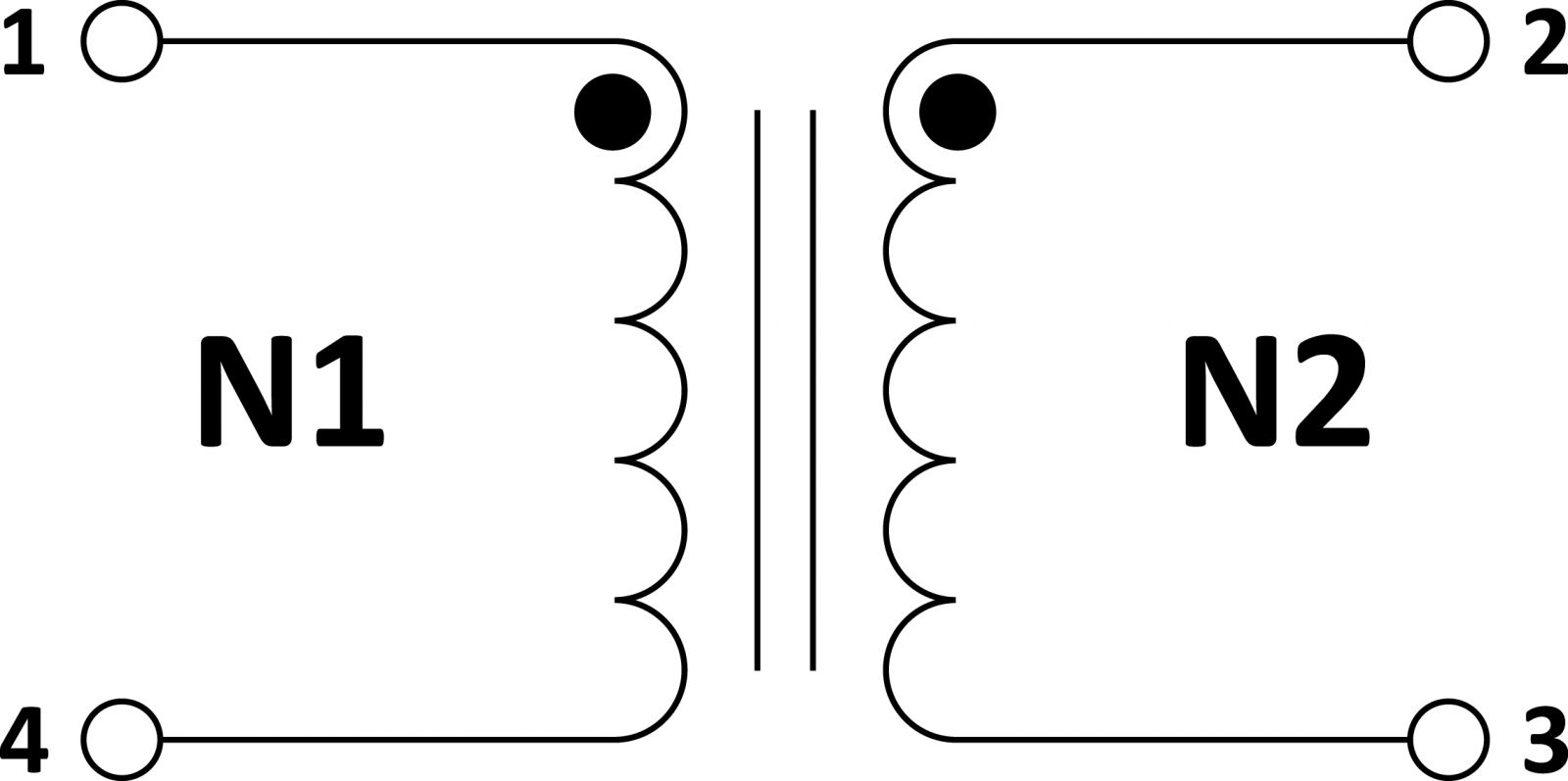
The main components of the transformer are the primary coil N1 and the secondary coil N2 and the core, the main functions are: voltage conversion, current conversion, isolation, impedance conversion, voltage regulation and so on.
When alternating current passes through a single winding of a transformer, the electricity generates a magnetic force.
The function of the iron core is to guide the magnetic field path of the primary and secondary coils, conduct the magnetic field to the secondary coil, force the charge Q in the coil to move, and then form an electromotive force “ε”, generate current “I”, and obtain energy “W”.
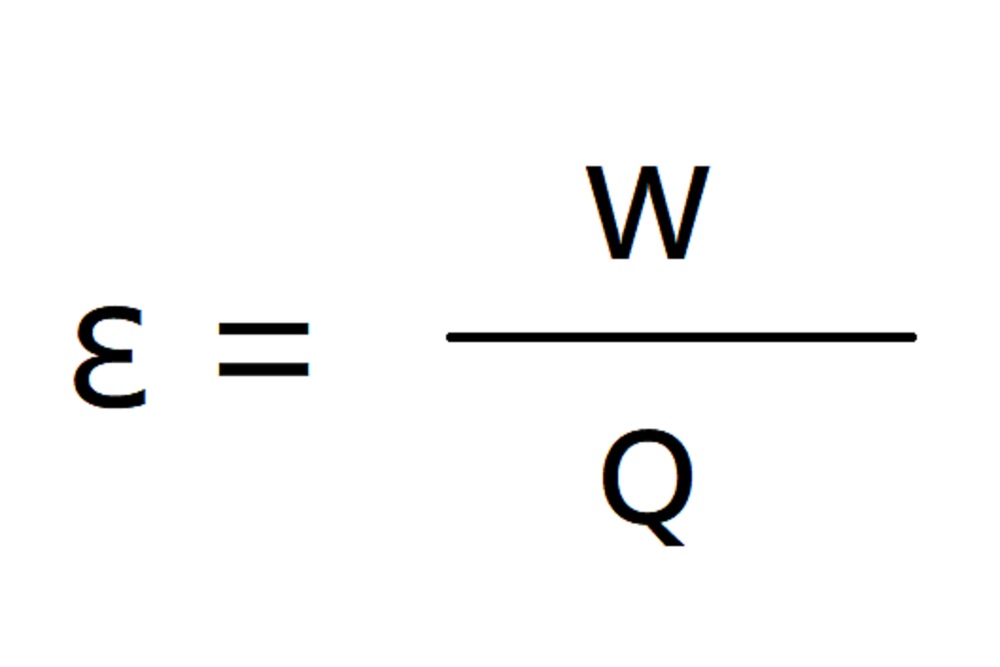
Transformer losses are divided into iron loss (iron core) and copper loss (coil), and the loss is converted into thermal energy to cause temperature rise.
The role of the iron core is to strengthen the coupling between the two coils. In order to reduce iron losses, hysteresis losses and eddy-current losses need to be reduced in the core.
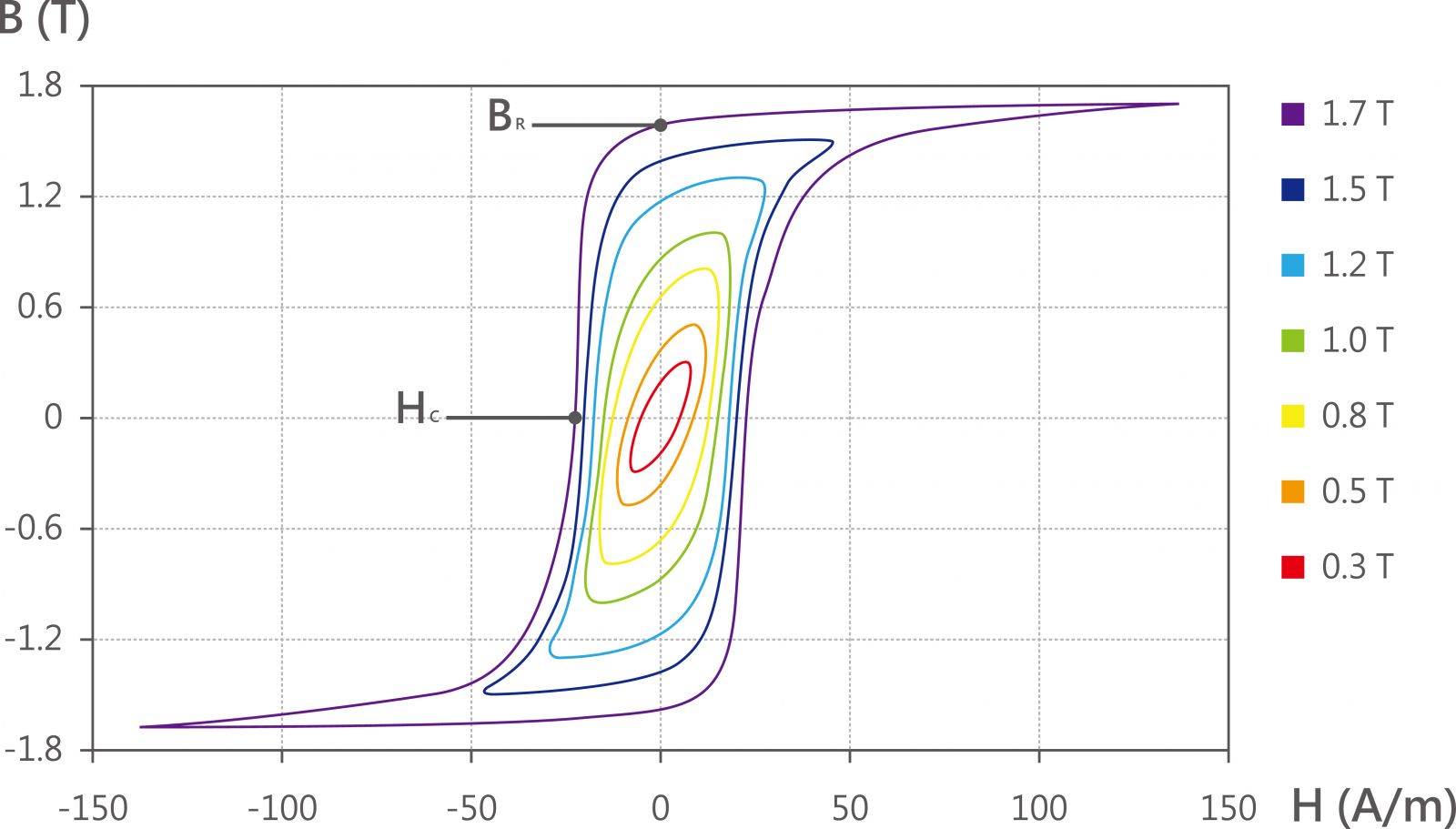
Hysteresis losses, related to the core material, when the electromagnetism, the magnetic filed of the iron core changes, the magnetization strength will also change, can be judged from the B-H curve, the larger the curve area, the greater the hysteresis loss.
The relationship between the magnetic field strength (H) and the magnetic induction intensity (B) of the magnetic material is nonlinear.
If the relationship between the two will rise to a certain point in a curve under the condition of enhanced magnetic field strength, after reaching this point, even if the magnetic field strength H continues to increase, the magnetic induction intensity B will no longer increase.
This condition is called magnetic saturation.
BR means residual magnetism, which means that after the magnet is magnetized to saturation, the external magnetic field is removed, and a certain magnetization strength can still be maintained in the direction of the original external magnetic field.
HC is an coercive force, and the magnetic material has been magnetized to magnetic saturation, and the magnetic field strength required to reduce its magnetization intensity to zero is required. Ferromagnetic materials with low coercive force are called soft magnetism.
Eddy-current losses, electromagnetism, produces eddy currents moving in the core, the resistance of the core material while heat dissipation, eddy current loss and the size of the current circulation area are proportional to the size.
The main functions of the transformer are three: boost, buck, and isolation.
As long as the ratio of turns on both sides of the coil is adjusted, the voltage rise and fall can be achieved.
If the transformer has a primary winding coil turn of 5 and a secondary winding turn of 10, a 1:2 boost transformer is formed, which means that the voltage is doubled after being conducted from the primary winding to the secondary winding. Conversely, if the number of primary winding coil turns is 10 and the number of secondary winding turns is 5, a 2:1 step-down transformer is formed, halving the voltage.
With these basic knowledge, transformers are actually quite simple devices. There are a wide range of transformer types, including power, isolation, signal handling, current sensing and other types.
Related articles :
• APPLE MagSafe tangle dancing with Qi2 MPP
• What is copper loss? What is the skin effect ? The difference between Isat and Irms
• What is an inductor?
 GOTREND Technology Co.,Ltd
GOTREND Technology Co.,Ltd